Business Expertise
This article is based on doing business processes, such as buying, selling goods and invoicing. The software in this article is the SAP system as I have been doing multiple projects and changes in this system as a business consultant for various customers for many years.
Introduction
What is a business process? This is a way of working within a company for certain activities, like for example,
And so on. Each company has different things going on within different departments in their organization.
Business processes often have process steps and details. For example,
They can be simple as for a standard 'Order to Cash' (OTC) process flow,
Or be more complex like,
Many years ago many companies had standard business processes which they used without even being aware of them. Many people daily did their part of the work in the organization.
However, the last few decennia with advanced computer systems, technology and increasing of the international markets, companies have been inventarising & improving many of their daily ways of working. Gradually there have been needs for new different processes, for example for overseas trade and taxes.
For example in the old days, when a customer needed a few pallets, some companies were more than willing to just lend them out or give them. Nowadays, the idea makes some employees nervous, having to register a non-profitable thing in the system. Maybe they have to adopt a new returns process or consignment process to temporarily transfer the palets.
Increased business caused many companies to struggle, their processes going awry, due to lack of communication, lack of familiarity with the computer software, not knowing what to do in certain exception cases and so on.
Another example with the overseas trade, goods can be produced in portugal, sold in Norway and the main company may be located somewhere in Singapore. Who should be taxed and how high should the taxes be? Even more complex is it when part of the production is outsourced to another country like Marocco because it is cheaper for some steps of the production process to be done there.
To identify all the steps, content and responsibility of these processes can be extruciatingly complex. Moreover, how can the management in Singapore get a correct report each month of all the revenues and costs?
Do all steps need to be defined or inventarized? No, not at all. If a department chooses to do some activities like paying vendor invoices outside of their standard SAP system, they can.
What does a consultant do?
A business advisor or a consultant gives advice on how to create, change or update business processes and process steps.
Here the roles of business analysts, consultants, project managers, IT architects and so on come into the picture to identify the many processes, gather new requirements, and get them streamlined to optimize their use within the company and where needed.
Some companies hire such resources as internal advisors, while others sign a contract with an external consultancy company to do a large project.
A good consultant asks direct questions, stays positive, confident an respectful. He or she is empathic, knows how to connect people, processes and follows up, keeping track of the involved deadlines.
A good consultant is also creative and technical because questions from the business have to be translated to solutions, or not.
A consultant things in concrete measurable savings which will pay back the investments if the business decides to have the implementations done,
Here is an example when a purchase process has to be implemented in a company, I sometimes compare it with someone's own house.
Say for example I would classify my househould as being a part of SAP Materials Management.
- 0001 - Living Room
- 0002 - Kitchen
- 0003 - Hallway
When however, I do have to specify where I put the goods , as my wife wants to know, I make warehouse storage types and storage bins, like the fridge, freezer, the upper shelf, the lower shelf, the closets, and so on. Simply said, I add a level of detail where a manager, in this case my spouse, can report on.
This is just an example of classification, it's great to be creative.

Definition
There are different types of requirements I have done within a company,
- Projects
- Change Requests
- Services
- Incidents & problem management
These requirements can impact one or more of the following areas,
- Business documents - transactional data, orders, invoices, etc.
- Master data - material, customer, pricing data
- Reporting - lists of combined data
- Process flows - which process steps
Requirements
Whatever new issue or thing needs to be solved or setup, it's always necessary to get the requirements clear. It is relevant to ask some questions,
- What exactly is needed to be changed or fixed?
- Why do you want it changed, what is the reason?
- Where or in what areas is the change needed?
- What is the impact? Is it local or regional, does it concern a few or many people?
- Does it impact other business processes or ways of working?
- What is the urgency, are people hindered in their working now or can it wait?
- What is the priority? How fast does it need to be done? Can other processes go first?
- What resources are available, where and when?
- When does it need to be done, in which timeframe?
- Can we replicate the requirement or issue? Can we do it in the test environment?
- Who are the responsible contacts/ key users?
- Is there financial or legal impact?
Many people ask too little information. To have a good clarity saves a lot of time and having to come back many times over. Also make sure it is agreed on & registered so that the users will not come up with 'extra requirements' on the last moment, causing potential delay to what you are working on.
Always ask for an example and points of contacts. This is very important because else the requests stays too vague and the advisor may have to search around for hours.
- Do you have an example?
- Which departments/ business contacts/ key users are involved?
An advisor also occasionally has to challenge the business because the business isn't always innocent. Sometimes they are in a hurry, don't look well at things and come with an unreasonable request that will cost many hours and is just a nice thing to have. In this case the advisor has to ask counter questions, or just say no.
Examples of questions,
- How many times does the issue occur per month?
- What is the volume of data per month?
- What is the amount of money we are talking about per month?
- Is there a workaround possible? How much time does the workaround take?
- Is there an alternative solution?
- What is the risk of not having the change/ solution?
If there are only a few orders per month, or just one customer, the advisor may have to reject the change request because it's simply too small and not beneficial.
However, if the one customer is a very large or important customer, then the advisor may have to reconsider...
Process Steps

Once there is clarity on the requirements and approval, it's good to make a plan and do your improvements step by step, for example,
1. Definition - Define the project scope, goal, restrictions
2. Measuring - inventarise the requirements
3. Time Schedule - setup a time planning
4. Team Charter - Assign the team/ group
5. Analysis - examine the requirements and possible solutions
6. Development/ Implementaton - Build the solution
7. Unit Testing - do technical and functional testing
8. Acceptance testing - let the business do testing
9. Cut over plan - inventarize each activity needed to be done, configuration, development, master data, etc.
10. Approval - after succesful testing, gather approvals for the solution going live
11. Go live phase - Implement the solution
12. Control & Maintenenance - user manuals, training sessions, etc.
Solutions
Solutions can be,
Business Processes
Some examples of different business processes are written here below. Please note all these business processes relate to the SAP system, but of course can also be used outside of the SAP environment.
Sales & Distribution (SD-LE)

Sales & Distribution Processes (SD)
Order to Cash Process (basic)
Process Area: Sales & Distribution (SD)
Purpose: a standard business process to sell goods to a customer
1. Sales Order - Create an order to sell goods for a customer who ordered a product
2. Outbound Delivery - Create a delivery document to ship the goods to the customer
3. Sales Invoice - Create a billing document to invoice the customer who bought your goods
Order to Cash Process (contract)
Process Area: Sales & Distribution (SD)
Purpose: a standard business process to sell goods to a customer
1. Quotation - Create a quotation of offering a proposal to a potential customer
2. Contract - Create a definitive contract of the goods or service you are providing and in which timeframe
3. Sales Order - Create one or more sales orders to sell goods for a customer who holds the contract
4. Outbound Delivery - Create a delivery document to ship the goods to the customer
5. Sales Invoice - Create a billing document to invoice the customer who bought your goods
Order to Cash Process (extended)
Process Area: Sales & Distribution (SD)
Purpose: a standard business process to sell goods to a customer
1. Sales Order - Create an order to sell goods for a customer who ordered a product
2. Sales Order Confirmation - Send out confirmation of the received sales order to the customer, by generated message output through E-Mail, EDI, etc.
3. Sales Order Release - sales document can be released by status profile
4. Sales Order Credit Check - check to see if the customer of the sales order has enough credit limit
5. Outbound Delivery - Create a delivery document to ship the goods to the customer
6. Delivery Picking - pick the available goods from the shelves in the warehouse and add them to the picking list
7. Delivery Packing - pack the selected goods
8. Delivery Confirmation - Delivery can be confirmed
9. Transport planning - Delivery can be planned for transport
10. Post goods issue - When the truck with the goods has left the premisis, the goods are deducted from the stock
11. Sales Invoice - Create a billing document to invoice the customer who bought your goods
12. Accounting document - Display the financial document with the debit/ credit G/L accounts that is generated from the invoice
Order to Cash Process (interface)
Process Area: Sales & Distribution (SD)
Purpose: a standard business process to sell goods to a customer with EDI functionalities
1. Customer places order - Customer places a (purchase) order in their system or places an order online through a portal
2. Interface - Order is transferred to the interface and forwarded to the correct destination. Often the message format is also converted
3. Company Middleware - Our own middleware picks up the message and translates it further
4. EDI Sales Order - Sales Order IDOC is generated in our system
5. Sales Order - If the IDOC was posted correctly, a sales order is automatically created in our system
6. Outbound Delivery - Create a delivery document to ship the goods to the customer
7. EDI Dispatch Advise - Delivery document is sent to an external warehouse if picking and packing is needed, or send to an external logistics company (3PL) if supply planning & truck planning is not done by our own company
8. EDI Shipping/ Warehouse Confirmation - operations such as picking, packing, transport planning, post goods issue, and so on are confirmed and sent back to our system. There can be different IDOCs sent together or one IDOC at a time
9. Delivery update - Delivery status gets updated in our system by the IDOCs
10. Sales Invoice - Create a billing document to invoice the customer who bought your goods
11. EDI Invoice - Electronic invoice is sent to the customer by IDOC
12. Accounting document - Display the financial document with the debit/ credit G/L accounts that is generated from the invoice
Material Management (MM)
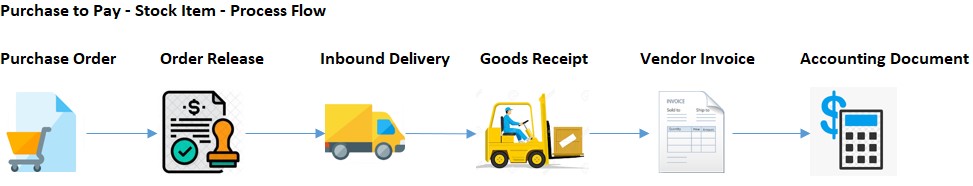
Purchase to Pay Process (basic)
Process Area: Material Management (MM)
Purpose: a standard business process to buy goods from an external vendor
1. Purchase Order - Create an order to buy goods from the vendor
2. Goods receipt - Receive the goods on our company stock
3. Vendor Invoice - Receive and process the invoice that the vendor sent your company to pay for the bought goods
Purchase to Pay Process (extended)
Process Area: Material Management (MM)
Purpose: a standard business process to buy goods from an external vendor
1. Purchase Requisition - Create a pre-request to order goods. This document can be used for planning and can a lso be automatically generated by material requirements planning (MRP)
2. Purchase Order - Create an order to buy goods from the vendor. Make sure your confirmation keys are correct which determine if a delivery needs to be done or not or only a goods receipt confirmation
3. Purchase Order Release - The document has to be approved by a manager or higher, depending on the total price of the ordered materials
4. Inbound Delivery - Create delivery document to deliver the goods to our premisis
5. Goods receipt - Receive the goods on our company stock. The goods receipt process can also be split in,
- Goods receipt into blocked stock
- Goods receipt transfer from blocked stock to unrestricted stock
6. Vendor Invoice - Receive and process the invoice that the vendor sent your company to pay for the bought goods
7. Accounting document - Display the financial document with the debit/ credit G/L accounts that is generated from the invoice
Stock Transport Order
1. Stock Transport Purchase Order - Create order to move goods from one plant and storage location to another
2. Outbound Delivery - Create outbound goods movement document
3. Post goods issue - Post the outbound delivery goods issue at the source plant
4. Goods receipt - Post the goods receipt in the destination plant. This may also be a two steps validation
Subcontracting
1. Subcontracting Purchase Order - Create an order to send multiple components to an external company who will create one finished product for you.
2. Outbound Delivery - Create outbound goods movement document
3. Post goods issue - Post the outbound delivery to goods issue the components
4. Goods receipt - Post the goods receipt of the finished product
Manufacturing (MFG)/ Production Planning (PP)

Production Process (basic; make to stock)
Process Area: Production Planning (PP)
Purpose: a standard business process to manufacture goods on stock
1. Production Order - Create a 'Make to Stock' production order to manufacture goods. Schedule your production order with a start and finish date, check the operations to be done
2. Production Order Availability Check - check the available stock, stage the materials
3. Production Order Release - Approve your order to build the item
4. Production Order Print - Print the production order papers for the goods to be made and the material components to be used in which location
5. Production Order Confirmation - Confirm all operations/ tasks in the production order
6. Goods Movements - All components used are deducted from stock, the finished product(s) are added on stock. The goods movements can be done individually or as part of the previous production order confirmation step
7. Transfer Order - If your company maintains stock on warehouse level, if needed, transfers from and to the correct storage bin like the picking storage bin and production storage bin can be done
Production Process (basic; make to order)
Process Area: Production Planning (PP)
Purpose: a standard business process to manufacture goods per sales order
1. Sales Order - Create an order to sell goods for a customer who ordered a product
2. Availability check - an ATP (available to promise) check is done if there is enough stock and the sales order is scheduled. Also by the transfer of requirements, a requirement is passed to directly create a production order after saving the sales order. This is done without MRP planning
3. Production Order - Create a 'Make to Order' production order to manufacture goods
4. Production Order Release - Approve your order to build the item
5. Production Order Confirmation - Confirm all operations/ tasks in the production order
6. Goods Movements - All components used are deducted from stock, the finished product(s) are added on stock
7.. Outbound Delivery - Create a delivery document to ship the goods to the customer
8. Sales Invoice - Create a billing document to invoice the customer who bought your goods
9. Accounting document - Display the financial document with the debit/ credit G/L accounts that is generated from the invoice
Planning Process (basic)
Process Area: Production Planning (PP)
Purpose: a standard business process plan available stock together with all the different stock requirements through Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
1. Stock/ Requirements List - Check the list per material group, material and plant to see available stock. There can be a fixed stock there, stock needed by sales orders, stock to be planned by planned orders, stock components to be added by purchase requisitions/ purchase orders and finished stock products to be added by production orders
2. MRP Run - Carry out the Material Requirements Planning (MRP) for the materials and plants
3. Stock/ Requirements List - Look at the new stock situation. Stock should be rescheduled accordingly to optimally allocate it for the business documents. If additional stock is needed within certain dates of the planning horizon, planned orders or purchase requisitions are automatically generated
Long Term Planning Process (advanced)
Process Area: Production Planning (PP)
Purpose: a standard business process for planning stock through long term planning (LTP)
1. Long Term Requirements - Create planned requirements for a long term planning
2. Planning Scenario - Create a planning scenario for the period
3. Long Term Planning Run - Plan the materials through a LTP (long term planning) planning run, which is similar to a MRP run
4. LTP Stock/ Requirements List - Check the results of the planning run by viewing the available & planned stock
5. Copy planning version - copy the planning version to MRP
6. Copy simulation planning to MRP - copy the simulation planned orders from LTP to MRP
7. Stock/ Requirements List - Look at the new stock situation.
1. Independent Requirements (PIR) - Enter independent requirement quantities per planning version for a material, product group of requirements plan for maintaining demand management. For example each week we need 50 PC of material 10000 and 30 PC of material 10001
2. MRP Run - Carry out the Material Requirements Planning (MRP) for the materials and plants
3. Stock/ Requirements List - Look at the new stock situation. Stock should be rescheduled accordingly to optimally allocate it for the business documents. If additional stock is needed within certain dates of the planning horizon, planned orders or purchase requisitions are automatically generated
Inventory Management (IM)
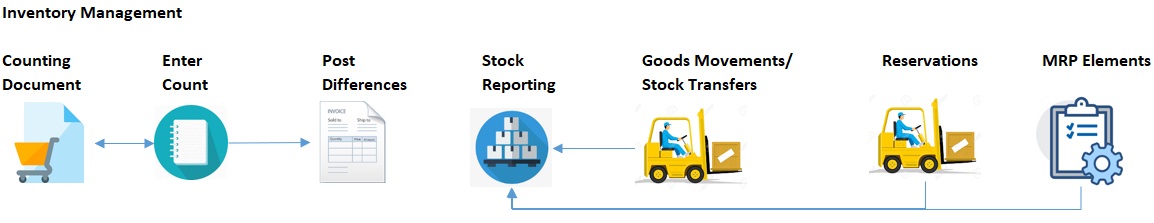
Stock Counting Process (basic)
Process Area: Inventory Management (MM)
Purpose: a standard business process to count the stock in different plants and storage locations
1. Counting Document - Create a document used for counting stock levels. Enter the material numbers (material names), plant and storage locations to be counted
2. Enter Count - Inventorise the stock in the warehouse and enter the actually counted quantity
3. Post Differences - Post the differences between the current stock and the count stock. A goods movements document with the quantity difference (positive or negative) should be made
4. Print Differences - Print list of stock differences
5. List Stock - Check your modified stock levels after the inventory differences
Warehouse Management (WM)

Transfer Order Process (basic)
Process Area: Warehouse Management (WM)
Purpose: a standard business process to transport goods from one warehouse location to another
2. Transfer Requirement - Create a requirement documet to move goods from one storage bin to another. This usually happens automatically due to goods movements being done. Transfer requirement documents are optional, also direct transfer orders can be created
3. Transfer Order - Create a definitive document to transfer the goods
4. Transfer Order Confirmation - The goods are moved from one storage bin to another within the warehouse
5. List Storage Bin Stock - List the amount of stock per storage bin
Quality Management (QM)

1. Goods receipt - receiving new goods on stock from for example a purchase order or production order
2. Change Inspection Lot - change the to be inspected materials lot and status
3. Results Recording - record the results, like the characteristics values such as temperature, humidity, power etc. depending on the type of product
4. Defects Log - log any defects found during inspection of the materials
5. Usage acceptance - decide if you want to accept the goods or not
Quality Notification
1a. Sales Order - create sales order document
1b. Purchase Order - create purchase order document
1c. Production Order - create production order document
2. Quality Notification - create an issue or defect depending on one of the above documents
3. Quality Notification - create a follow up action depending on the notification, like create a sales order to give goods to the customer, create a returns delivery to return purchased goods, etc. Put the status to in process
4. Document flow - the responsible department should process created the follow up documents
5. Quality Notification - put the status to complete once everything is done
Conclusion
Please note that business processes may vary a lot depending on the business requirements, the processes that are already in place, the software, the available resources, the time to do it, the situation, and so on.
Stories
This is a list of SAP related documents, texts, stories,
Chris van Zuiden, 2024 (c)
CONNECT